- Multiple row subquery returns one or more rows to the outer SQL statement.
- You may use the IN, ANY, or ALL operator in outer query to handle a subquery that returns multiple rows.
Using IN operator
SELECT ord_num,ord_amount,cust_code, agent_code FROM orders WHERE agent_code IN (
SELECT agent_code FROM agents WHERE working_area='Bangalore'
);
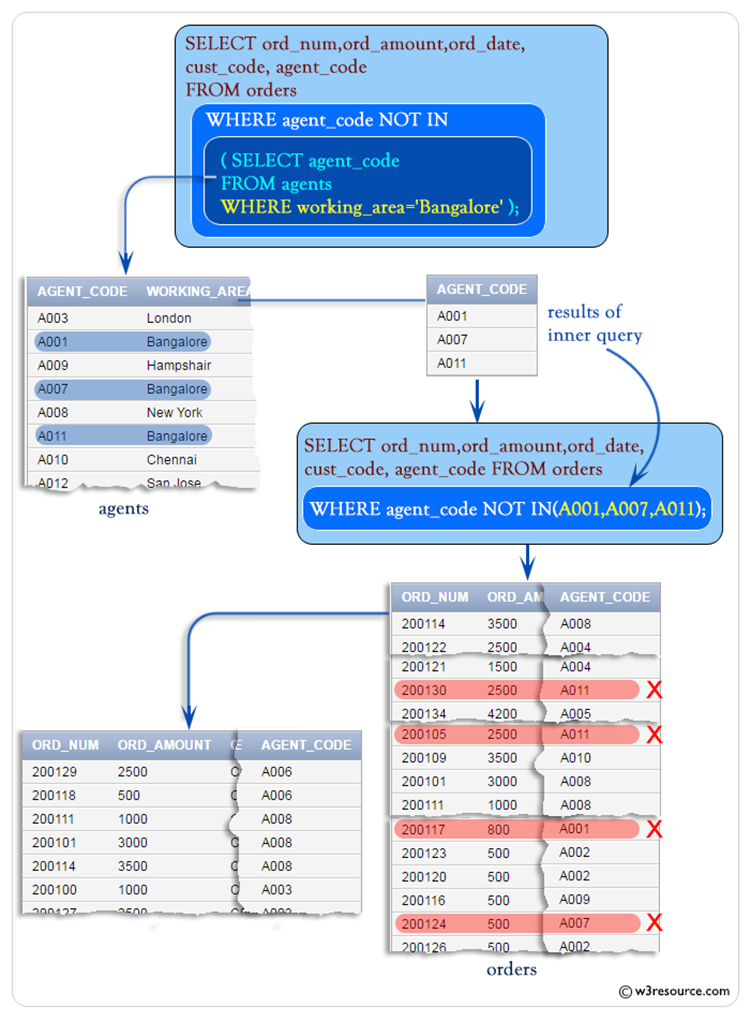
Using
NOT IN
SELECT ord_num,ord_amount,cust_code, agent_code FROM orders
WHERE agent_code NOT IN (
SELECT agent_code FROM agents WHERE working_area='Bangalore');
Using ANY
You can use the ANY operator to compare a value with any value in a list. You must place an =, <>, >, <, <= or >= operator before ANY in your query.
The following example uses ANY to check if any of the agent who belongs to the country 'UK'.
SELECT agent_code,agent_name,working_area,commission FROM agents
WHERE agent_code=ANY(
SELECT agent_code FROM customer WHERE cust_country='UK');
Multiple Column Subqueries
You can write subqueries that return multiple columns.
The following example retrieves the order amount with the lowest price, group by agent code.
select ord_num, agent_code,ord_amount from orders where (
agent_code, ord_amount) IN (
select agent_code, MIN(ord_amount) from orders group by agent_code);